Explain the Structural Differences Between Alkanes Alkenes and Alkynes
The alkanes are also called as paraffins. An unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carboncarbon triple bond between two carbon atoms.
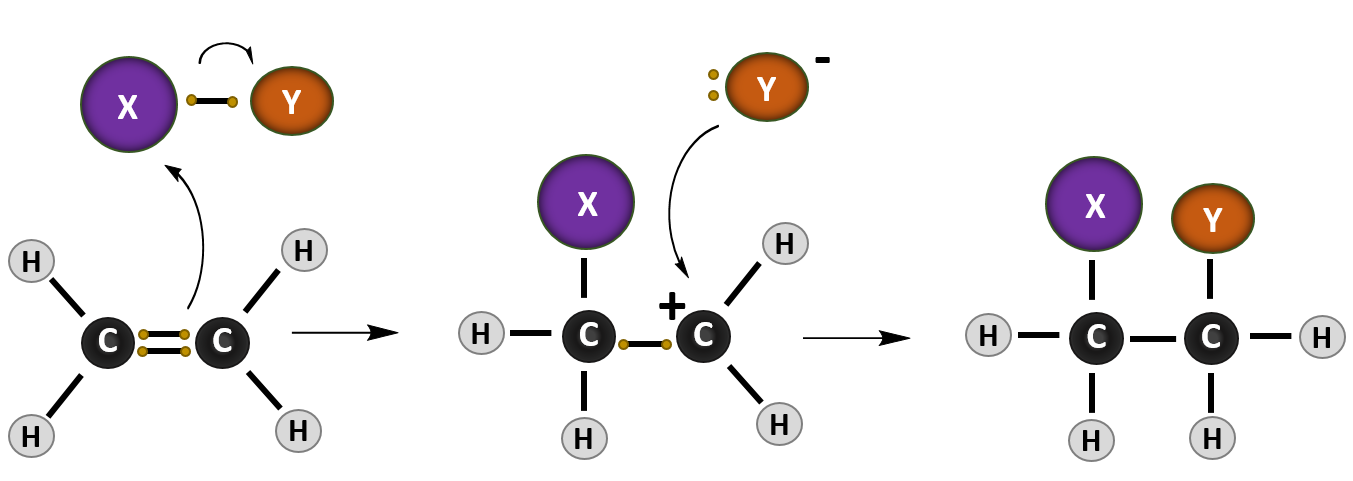
Ch105 Chapter 8 Alkenes Alkynes And Aromatic Compounds Chemistry
Alkynes Alkynes are also unsaturated hydrocarbons.
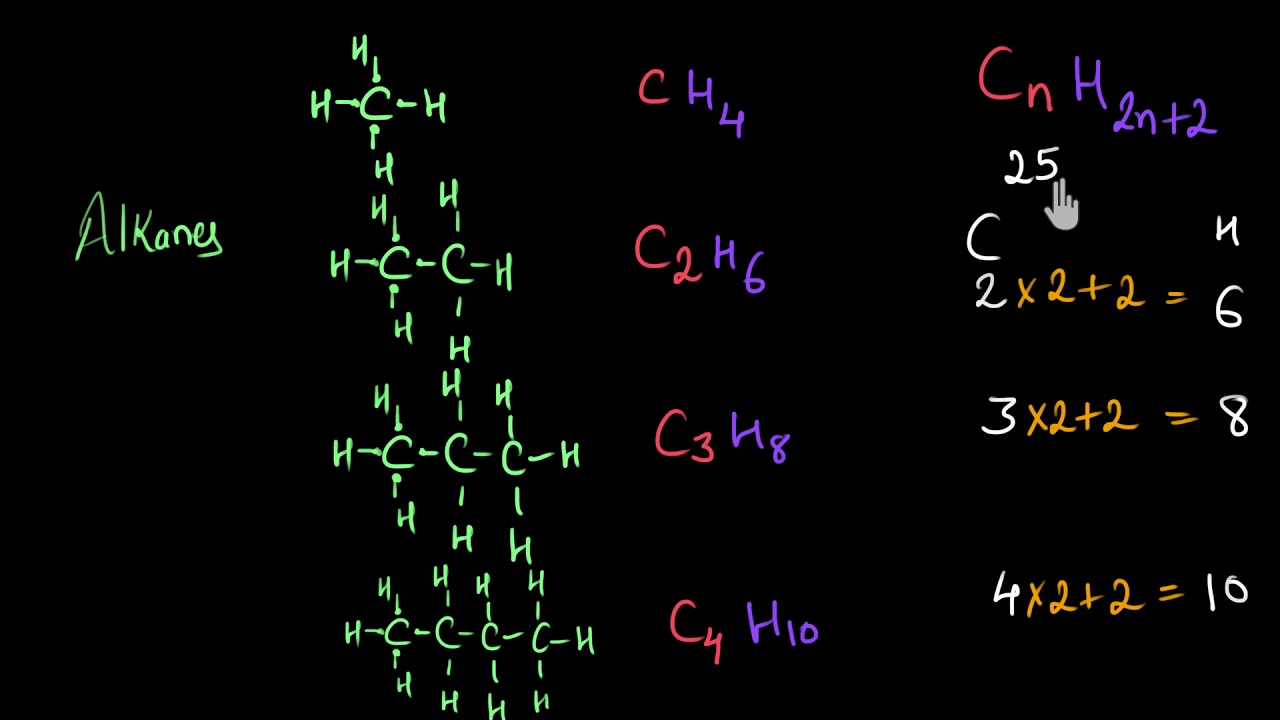
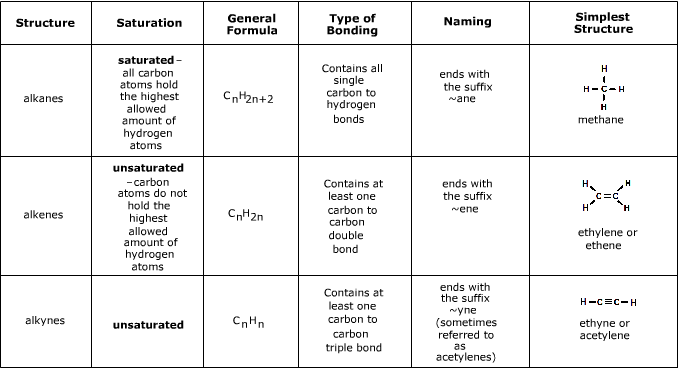
. The general formula is CnH2n which is two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane. The alkenes have at least one carbon-carbon double bond and the alkynes have at least one. 2General formula for alkanes is CnH2n2.
Meaning a single bond between the carbon atoms. Answer 1 of 5. Between them by a straight line.
Alkanes and alkenes are such two categories. Each alkene has 2 fewer electrons than the alkane with the same number of carbons. They undergo addition and oxidation reactions readily.
Alkanes Alkenes Alkynes Learning Check Page 19 8-12 8. The general formula for Alkynes is C n H 2n-2. C X n H 2 n 2.
Moreover Double bond carbons are sp 2 hybridized in alkenes and triple bond carbons are sp hybridized in alkynes. General formula for alkenes in the case of a non-cyclic compound is CnH2n. How do you remember the differences between alkanes and alkenes.
3Alkanes are the most stable hydrocarbons as the carbon. Alkynes are hydrocarbons compounds containing only C and H that have one or more triple bonds two C atoms are. Toluene is classified as an aromatic compound.
Alkane- They are hydrocarbons which are joined by single bonds only. EACH OF THESE FORM A HOMOLOGOUS SERIES A GROUP OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS HAVING A COMMON GENERAL FORMULA OR IN WHICH EACH. Explain the difference between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Both these types of hydrocarbons are composed of branched unbranched and cyclic hydrocarbons. Thus called as saturated hydrocarbons They are less reactive in nature as the carbons bonds are stableThey are also called paraffins They are simplest of the hydrocarbons which have no functional groups attached to the carbon atoms. Notice that the molecular models on the right show that the bonds are not really at angles of 90.
In an alkane all 4 4 4 valencies of the carbon atom are satisfied with other hydrogen atoms. Draw the structure of toluene CH. Alkanes CnH2n2 Alkenes CnH2n Alkynes CnH2n-2 3.
Alkenes have the pi bond between the carbon atoms and during a lot of reactions the pi bond ruptures in order to form a single bond thus they are more reactive than alkanes but relatively stable as compared to alkynes. A π bond being a weaker bond is disrupted much more easily than a σ bond. ALKANES ALKENES ALKYNES AND CYCLOALKANES ARE HYDROCARBONS COMPOUNDS CONTAINING ONLY CARBON AND HYDROGEN.
An alkane is a saturated hydrocarbon. It has the potential to react with bromine. Toluene is the common name of methylbenzene.
Alkenes are much more reactive than alkanes because the C C CC moiety is a reactive functional group. They are more reactive than alkanes and alkynes due to the presence of two π bonds. 1Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons.
This is a saturated molecule as it needs the most hydrogen because only single bonds are evidentEg. Additionally it is meaningless to say that alkenes are more reactive than alkynes without specifying reactivity towards what. Alkenes are hydrocarbons compounds containing only C and H that have one or more CC double bonds two C atoms are linked by 4 shared electrons.
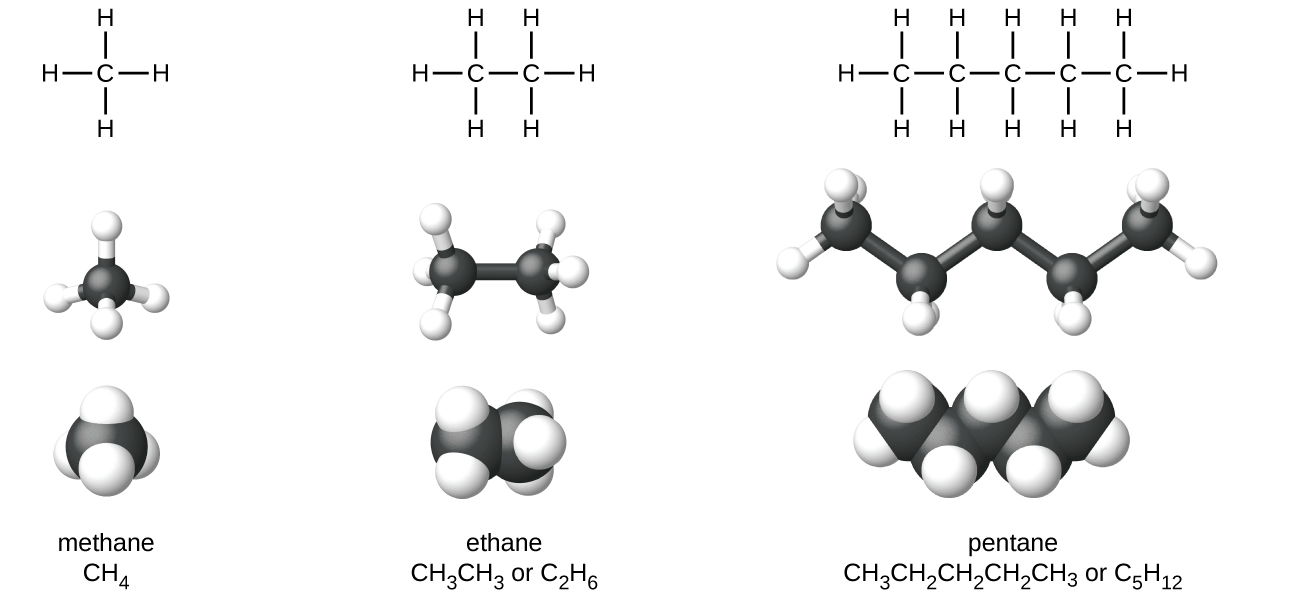
Methane gas is the first member of the homologous series of alkanes. Alkenes are hydrocarbons that contain one or more double bonds while alkynes contain one or more triple bonds. The two π systems in alkynes are orthogonal so their energy is not reduced by interaction with each other.
Draw the distinguishing structural feature for the following. Explain what that means. The main difference between alkanes and alkenes is that alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons whereas alkenes are.
This gives them a general formula. Alkanes and Alkenes are two types of hydrocarbon families which contain carbon and hydrogen in their molecular structure. A further difference between alkenes and alkynes is that the alkenes have no acidic hydrogen.
They have one or more triple bonds between the carbon atoms. One of a set of the isomers of a compound that exhibits stereoisomerism. Alkanes have no.
The key difference between Alkanes and Alkenes is their chemical structure. Organic Chemistry Ways to Draw and Represent Molecules Condensed Structure. However theres something else in play here.
1 Answer anor277 Jun 7 2018 These differ by their degree of unsaturation. Alkanes is a molecule that only contains single bonding between the carbon and hydrogen atoms. Alkynes are the base materials used for making organic compounds.
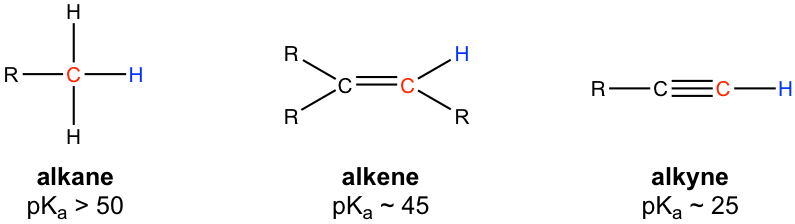
One important property of alkynes is the acidic nature of the hydrogen attached to the triple bonded carbon because hydrogen is attached to sp hybridised carbon. As explained since there is a bigger volume to an alkane than its corresponding alkyne ie. C X n H 2 n 2.
What is the difference between alkanes alkenes and alkynes. Alkanes alkenes alkynes aromatics 3. Alkanes have single bonds between carbon atoms.
Alkynes are molecules that have a triple bond between two carbon. The first stable member of alkynes is Ethylene C 2 H 2. A π bond being a weaker bond is disrupted much more easily than a σ bond.
Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons with the general molecular formula of C n H 2n2 and alkenes are said to be an unsaturated hydrocarbon group since they contain. Exams Prep Master Updated On - Jan 21 2022. With the same number of carbons the alkane should have a higher boiling point.
The key difference between alkenes and alkynes is that the alkenes have carbon-carbon double bonds whereas alkynes have carbon-carbon triple bonds. It means that is it saturated with hydrogens or bonded to as many hydrogens as possible. Alkynes have a TRIPLE bond.
Alkynes are unsaturated compounds that have at least one triple bond. Below are the differences between the four stated as a list. First of all alkanes alkenes and alkynes are all hydrocarbon molecules which means they only contain carbon and hydrogen atoms.
There are reactions that alkenes wont do which alkynes will and vice versa. Here are the names and structures of five alkanes. The alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons and all the bonds between carbon atoms are single bonds.
Properties of Hydrocarbons Alkanes alkenes alkynes and aromatic hydrocarbons are similar in that all contain only hydrogen atoms and carbon atoms. Alkenes have double bonds between carbon atoms.

Difference Between Alkanes And Alkenes Dentalimplantsurgery Com Custom Academic Help
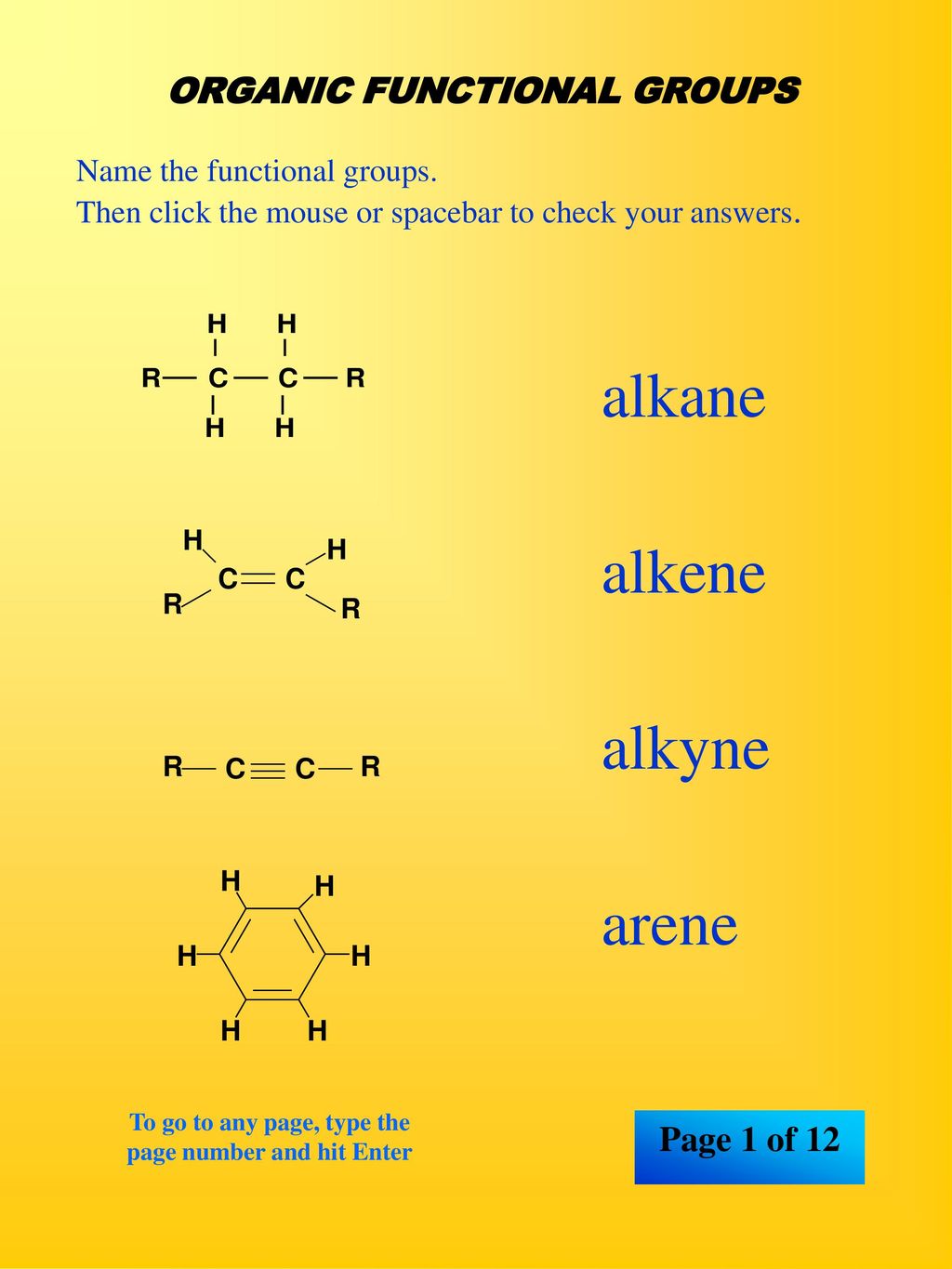
Alkane Alkene Alkyne Arene Ppt Download

Alkanes Alkenes And Alkynes General Molecular Formula Video Khan Academy

Introduction To Hydrocarbons Grade 12 Chemistry

Nomenclature Of Alkanes Alkenes And Alkynes Iupac Nomenclature Of Alkanes Alkenes And Alkynes

Solved 10 Alkanes Alkenes Alkynes And Aromatic Chegg Com
Difference Between Alkanes And Alkenes Definition Nomenclature Properties And Reactions
What Are The Differences Between Alkanes And Alkenes In Terms Of Physical And Chemical Properties Quora

What Are The Differences In Chemical Properties Between Alkanes Alkenes And Alkynes Possibly With Reactions Quora

Differences Between Alkane Alkene And Alkyne Youtube
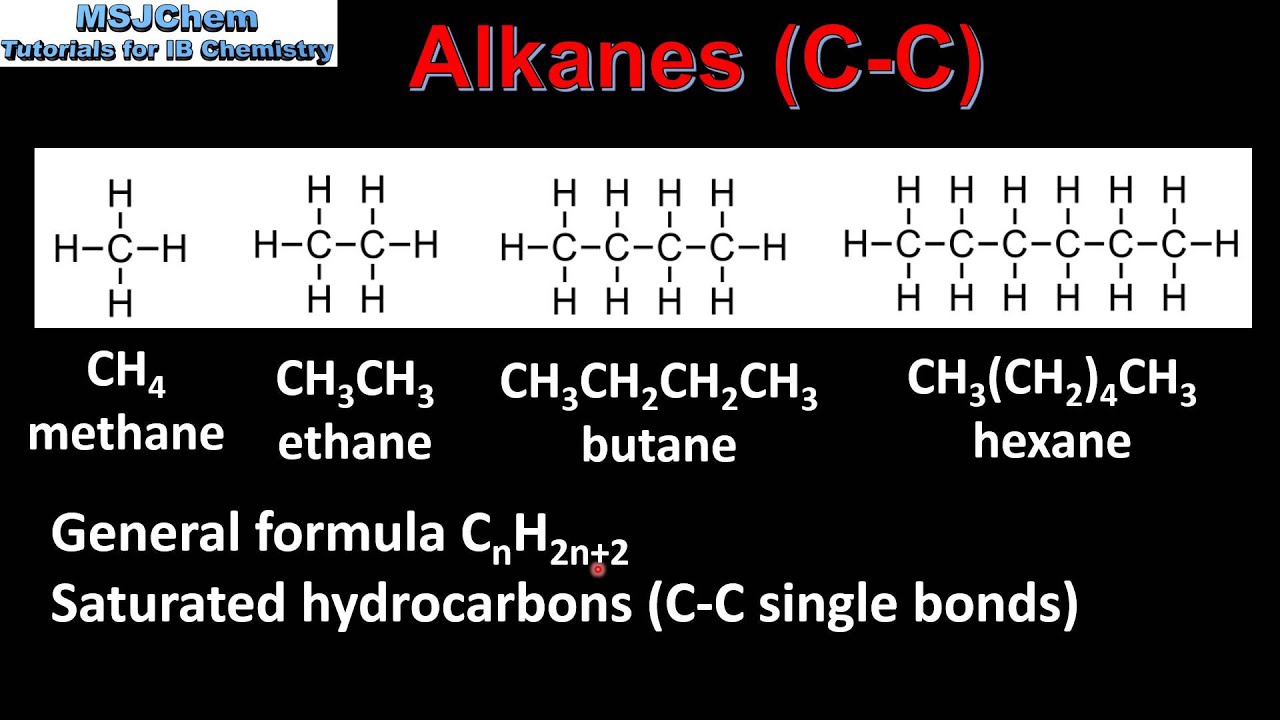
10 1 Naming Alkanes Alkenes And Alkynes Sl Youtube
Alkanes Alkenes Alkynes Brilliant Math Science Wiki

Compare And Contrast The Molecular Structures Of Alkanes Alkenes And Alkynes Include Trends In Melting Points And Boiling Points Name Draw And Construct Ppt Download
22 2 Alkanes Cycloalkanes Alkenes Alkynes And Aromatics Chemistry Libretexts
10 8 Alkynes Organic Chemistry I

Compare And Contrast The Molecular Structures Of Alkanes Alkenes And Alkynes Include Trends In Melting Points And Boiling Points Name Draw And Construct Ppt Download


Comments
Post a Comment